
These can be large or small, weakly acidic or basic, hydrophilic or hydrophobic, positively or negatively charged, or neutral. Different properties characterize each residue. Since enzymes are proteins, there is a unique combination of amino acid residues (also side chains, or R groups) within the active site. The location within the enzyme where the substrate binds is the enzyme’s active site. Two reactants might also enter a reaction, both become modified, and leave the reaction as two products. In others, two substrates may come together to create one larger molecule. In some reactions, a single-reactant substrate breaks down into multiple products. There may be one or more substrates, depending on the particular chemical reaction. The chemical reactants to which an enzyme binds are the enzyme’s substrates. * Enzyme Active Site and Substrate Specificity Enzymes facilitate chemical reactions by binding to the reactant molecules, and holding them in such a way as to make the chemical bond-breaking and bond-forming processes take place more readily. Almost all enzymes are proteins, comprised of amino acid chains. This way, the effect of pH on enzyme activity can be studied practically.Theme 4: How Do Diet, Exercise and Weight Affect Health?Ī substance that helps a chemical reaction to occur is a catalyst, and the special molecules that catalyze biochemical reactions are enzymes. Hence, for the chemical reaction to take place, you need to adjust the pH of the solution in such a way that it is suitable for both, the enzyme and the substrate. This occurs when there are changes in the structure of the active site and the substrate.

At times, you will notice that there is no reaction at all. Over here, the rate of reaction or the activity of enzymes will not be the same as the previous one. For more information on enzymes, you can refer to enzyme substrate complex.Ĭonsider a case when the reaction is adjusted at a pH level different from the optimum value. Also, the active site of the enzyme is changed, after which the substrate can no longer identify the enzyme. Ultimately, the chemical makeup of the enzyme and substrate are changed. These ions alter the structure of the enzymes and at times the substrate, either due to formation of additional bonds or breakage of already existing bonds.

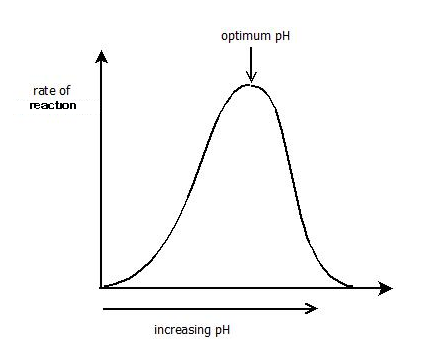
An increase or decrease in the pH changes the ion concentration in the solution.

To be more precise, pH indicates the concentration of dissolved hydrogen ions (H +) in the particular solution. When we study pH, it is clearly defined as the measurement for the acidic or alkaline nature of a solution.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
